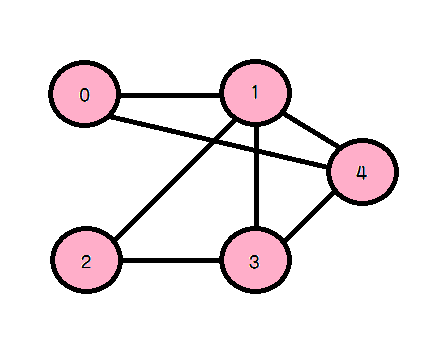
그래프(Graph) 란?
그래프란 비선형(non-linear) 자료구조이며, 노드(Node)와 엣지(Edge)로 구성되어있다.
- 노드(Node) : 노드는 꼭짓점(vertex)로 표현됩니다.
- 엣지(Edge) : 엣지는 두 노드를 연결하는 선(line)으로 표현됩니다.

위 그래프를 V(vertex) = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}, E(edges) = {01, 12, 23, 34, 04, 14, 13}으로 표현할 수 있습니다.
그래프는 많은 일상 생활의 문제점을 해결하기 위해 사용됩니다. (네트워크의 표현 등)
그래프의 표현
그래프를 인접 행렬(Adjacency Matrix) 또는 인접 리스트(Adjacency List)로 표현 할 수 있습니다.
- 인접 행렬

인접행렬은 2차원 배열(v x v)로 표현될 수 있습니다. 엣지가 존재하는 노드의 짝(i, j)의 배열 값을 1로 설정하고, 엣지가 존재하지 않는 노드의 짝(i, j)의 배열 값을 0으로 설정합니다. 가중치 그래프(Weighted Graph)에서는 배열 값을 w(가중치)로 설정 할 수 있습니다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 변수 선언
int vertex, **matrix;
// 정점(vetex) 개수 입력
cin >> vertex;
// 인접 행렬 동적할당 (v x v)
matrix = new int*[vertex];
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++) {
matrix[i] = new int[vertex];
}
// 인접 행렬 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertex; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 간선(edge) 입력 (-1 입력 시 종료)
while (1) {
int edge1, edge2;
cin >> edge1 >> edge2;
// 종료 조건
if (edge1 == -1 || edge2 == -1)
break;
// matrix 범위 초과
else if (edge1 > vertex || edge2 > vertex)
continue;
// 이미 연결 된 간선인 경우
else if (matrix[edge1][edge2] == 1 && matrix[edge2][edge1] == 1)
continue;
// 인접 행렬에 입력
matrix[edge1][edge2] = 1;
matrix[edge2][edge1] = 1;
}
// 인접행렬 출력
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertex; j++) {
cout << matrix[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
// 메모리 해제
for (int i = 0; i < vertex; i++) {
delete[] matrix[i];
}
delete[] matrix;
// 프로그램 종료
return 0;
}
2. 인접 리스트

각 꼭짓점(vertex)의 리스트는 헤더(Header) 노드를 가지비다. 각 헤더 노드들은 배열을 이용하여 연결된 각각의 노드를 순차적으로 가리킵니다.(오름차순)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 인접 리스트 구조체 선언
struct AdjListNode
{
int dest;
struct AdjListNode* next;
};
// 인접 리스트 헤더 구조체 선언
struct AdjList
{
struct AdjListNode *head;
};
// 그래프 구조체
struct Graph
{
int V;
struct AdjList* array;
};
// 새로운 노드 추가
struct AdjListNode* newAdjListNode(int dest)
{
struct AdjListNode* newNode =
(struct AdjListNode*) malloc(sizeof(struct AdjListNode));
newNode->dest = dest;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 그래프 생성
struct Graph* createGraph(int V)
{
struct Graph* graph =
(struct Graph*) malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->V = V;
graph->array =
(struct AdjList*) malloc(V * sizeof(struct AdjList));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; ++i)
graph->array[i].head = NULL;
return graph;
}
// 엣지 추가
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int src, int dest)
{
struct AdjListNode* newNode = newAdjListNode(dest);
newNode->next = graph->array[src].head;
graph->array[src].head = newNode;
newNode = newAdjListNode(src);
newNode->next = graph->array[dest].head;
graph->array[dest].head = newNode;
}
// 그래프 출력
void printGraph(struct Graph* graph)
{
int v;
for (v = 0; v < graph->V; ++v)
{
struct AdjListNode* pCrawl = graph->array[v].head;
printf("\n Adjacency list of vertex %d\n head ", v);
while (pCrawl)
{
printf("-> %d", pCrawl->dest);
pCrawl = pCrawl->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 5;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V);
addEdge(graph, 0, 1);
addEdge(graph, 0, 4);
addEdge(graph, 1, 2);
addEdge(graph, 1, 3);
addEdge(graph, 1, 4);
addEdge(graph, 2, 3);
addEdge(graph, 3, 4);
printGraph(graph);
return 0;
}'DevLog > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 비선형 자료구조 정리 (트리) (0) | 2021.01.22 |
|---|---|
| 선형 자료구조 정리 (배열) (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| 선형 자료구조 정리 (연결리스트) (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| 선형 자료구조 정리 (큐) (0) | 2021.01.20 |
| 선형 자료구조 정리 (스택) (0) | 2021.01.20 |